
Experience design concept and direction for Mobile Surgery
Design research and strategy: Vision for Mobile Viewing Station and C-arm hardware and software components
[NDA]: Due to non-disclosure agreement signed with the project stakeholders, only limited work is shared.
Tools used: Sketch, Miro, Sammie CAD
Group size: 2
TASK
-
Studying existing Information Architecture and workflow design
-
User experience research: Personas for different users, environment analysis, heuristic analysis
-
Designing new layout, information architecture, hardware strategy and workflows
-
Software visual design and usability evaluation
-
Ergonomics analysis
EXISTING WORKFLOW

Existing end to end workflow was studied and a high level wireframe was created consisting of different system states and different applications.
With the wireframe plotted, other than the emerging usability concerns, it was clear that the visual design needs to be updated to the latest design language system.
UX RESEARCH


With the understanding of the product, user research was carried on which aimed at empathising with the users and studying their positioning in the operation room.
The environment analysis showed that the positioning of the different users varies with the type of surgical procedure.
Hence, it is critical to distribute the information presented on different interfaces such that it aids the users and their location in operation room.
Multiple workshops/co-creation sessions were also conducted focusing on the usability issues in the different steps of the existing workflow.
These issues were further mapped on the effort vs impact chart to prioritise the backlog. The backlog was further categorised into feature enhancements and design enhancements.


DESIGN STRATEGY

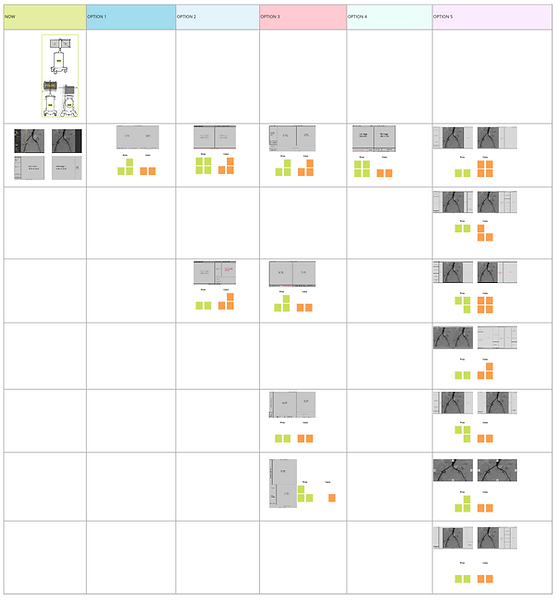
With the opportunities prioritised from effort vs impact chart, the user experience design was initiated which included working on enhancements to support better image quality and improved workflow design.
For better image quality, different configurations of the mobile viewing station's display monitors were considered. A co-create workshop was conducted to evaluate these configurations based on certain pre-defined metrics (cost to benefit, ergonomics, safety, technical feasibility, design harmonisation, UI layout etc.).

For improved workflow design, with the display monitor configurations fixed, a 'channel-touchpoint' matrix was framed. The matrix was used to fetch answers like what type of information would be displayed on which screen and at what step of the workflow. This matrix was further evaluated by stakeholders till the workflow design was mature.
SOFTWARE VISUAL DESIGN
After finalising the improved workflow design (in form of channel - touchpoint matrix), visual design was made.
Design components were imported from the new design language system's assets library.
Some key screens were designed keeping scenarios like maximum space utilisation, harmonisation with other Image Guided Therapy domains and visibility in operation room in mind.
These key screens were further evaluated. Usability testing was done.


Visual design started with Information Architecture (IA) followed by layout and wireframes.
Focus for IA, layout and wireframes was made for Touch Screen Module (TSM) as TSM's size was smaller than MVS.

MVS Concept A
This concept was designed focusing towards image viewing. Controls for processing the image were provided in the touch screen module (TSM).
1: Product Branding
2: Patient details
3: Clock time and date
4: Scan dose details
5: Status information

MVS Concept B
This concept was designed focusing towards image viewing and controls for processing the image as well.
All buttons and icons were made as per touch specifications i.e. 48*48 px.
1: Product Branding
2: Patient details
3: Clock time and date
4: Scan dose details
5: Status information
6: Processing tools

MVS Concept AB
This concept was designed focusing towards touch screen module screen hardware. The image(s) is shown along with controls for processing the image.
All buttons and icons were made as per touch specifications i.e. 48*48 px.
1: Patient details
2: Scan instructions
3: Processing tools
Post creation of visual design, the evaluation of designs were done using usability testing. Participants were shown multiple concepts and they were asked about their preference. Some questions were also asked related to visibility of design elements when the operation room (OR) is simulated.
EXPERIMENT DESIGN

Q.1: Considering the user is standing at the table side and the MVS is kept at a standard distance, please confirm if the size is ok of all the texts and icons present in header and footer. If not, would you like to reduce or increase the size? Roughly, how much?
Q.2: Considering the user is standing at the table side and the MVS is kept at a standard distance, please confirm if the size is ok of
A: Reference Image & Thumbnails
B: all the texts present in side tool bar
If not, would you like to reduce or increase the size? Roughly, how much?
Q.3: Considering the user is working on TSM, please confirm if the size is ok of all the elements and both images. If not, would you like to reduce or increase the size? Roughly, how much?
ERGONOMICS ANALYSIS

Other than software design, hardware design was also considered from ergonomics point of view.
Task and risk analysis was done for the C-arm and mobile viewing station trolley. While doing the analysis, end to end tasks and sub-tasks were considered - assembly/disassembly of dual monitor setup, transportation of trolleys, preparation and surgical procedure.

The risks and mitigations from the risk analysis were further investigated.
For risks, systems ergonomics modelling was done.
For mitigations, different anthropometric databases were considered. Percentile 1 Japanese women to Percentile 99 dutch male was considered as population.
The ergonomics specification/ mitigations were further taken into account for digital human modelling. Sammie CAD was used for the same.
 C-arm handle |  Reach cone |
|---|---|
 Reach |  Handle push pull |